Activities
The research conducted at the TechnoLab falls within two major areas : Satellites observations and and physical-mathematical modeling.
Volcanic hazards monitoring from space
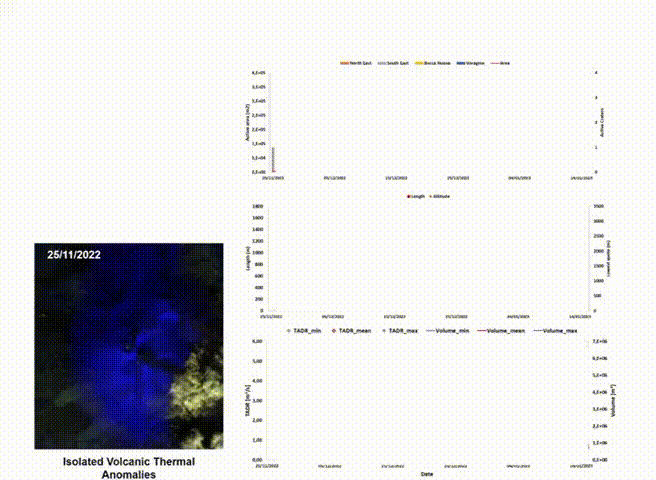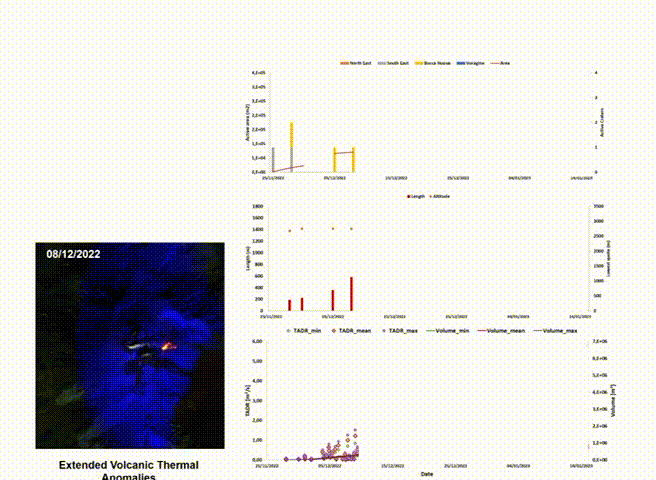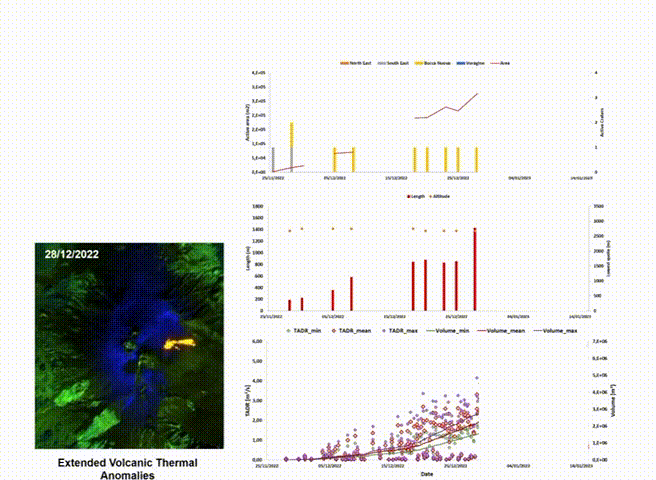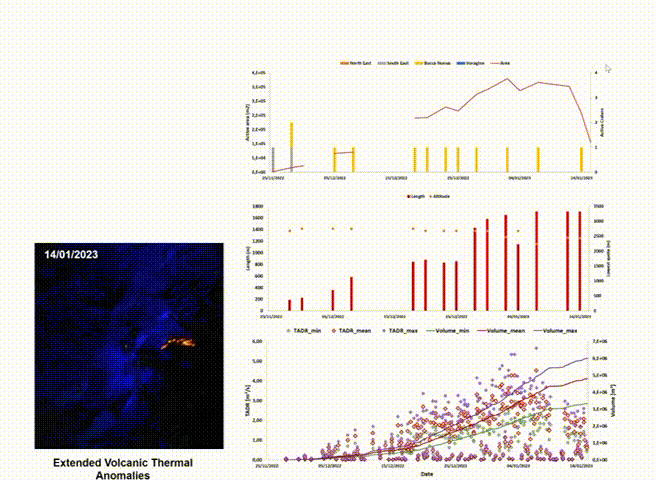 This division primarily works on the analysis of satellite images, which constitutes an essential tool for monitoring volcanic activity, providing frequent observations at low cost (fig: automatic processing of satellite for Etna volcano), even in areas that are difficult to detect from the ground. We develop and applies satellite techniques aimed at volcanic monitoring to identify, characterize, and track volcanic events and, therefore, derive the input parameters of the physical-mathematical models used to reconstruct the evolution of potentially hazardous volcanic phenomena. The increasing availability of open-source satellite data, with continuously improving temporal, spatial, and spectral resolutions, along with current developments in cloud computing and machine learning algorithms, a type of artificial intelligence where computers learn from data, promise to make volcanic hazard monitoring from space possible. We aim at integrating traditional ground-based volcanic monitoring with technological innovations in satellite observations and artificial intelligence methods to develop a better understanding of hazardous phenomena associated with volcanic eruptions.
This division primarily works on the analysis of satellite images, which constitutes an essential tool for monitoring volcanic activity, providing frequent observations at low cost (fig: automatic processing of satellite for Etna volcano), even in areas that are difficult to detect from the ground. We develop and applies satellite techniques aimed at volcanic monitoring to identify, characterize, and track volcanic events and, therefore, derive the input parameters of the physical-mathematical models used to reconstruct the evolution of potentially hazardous volcanic phenomena. The increasing availability of open-source satellite data, with continuously improving temporal, spatial, and spectral resolutions, along with current developments in cloud computing and machine learning algorithms, a type of artificial intelligence where computers learn from data, promise to make volcanic hazard monitoring from space possible. We aim at integrating traditional ground-based volcanic monitoring with technological innovations in satellite observations and artificial intelligence methods to develop a better understanding of hazardous phenomena associated with volcanic eruptions.
Modeling
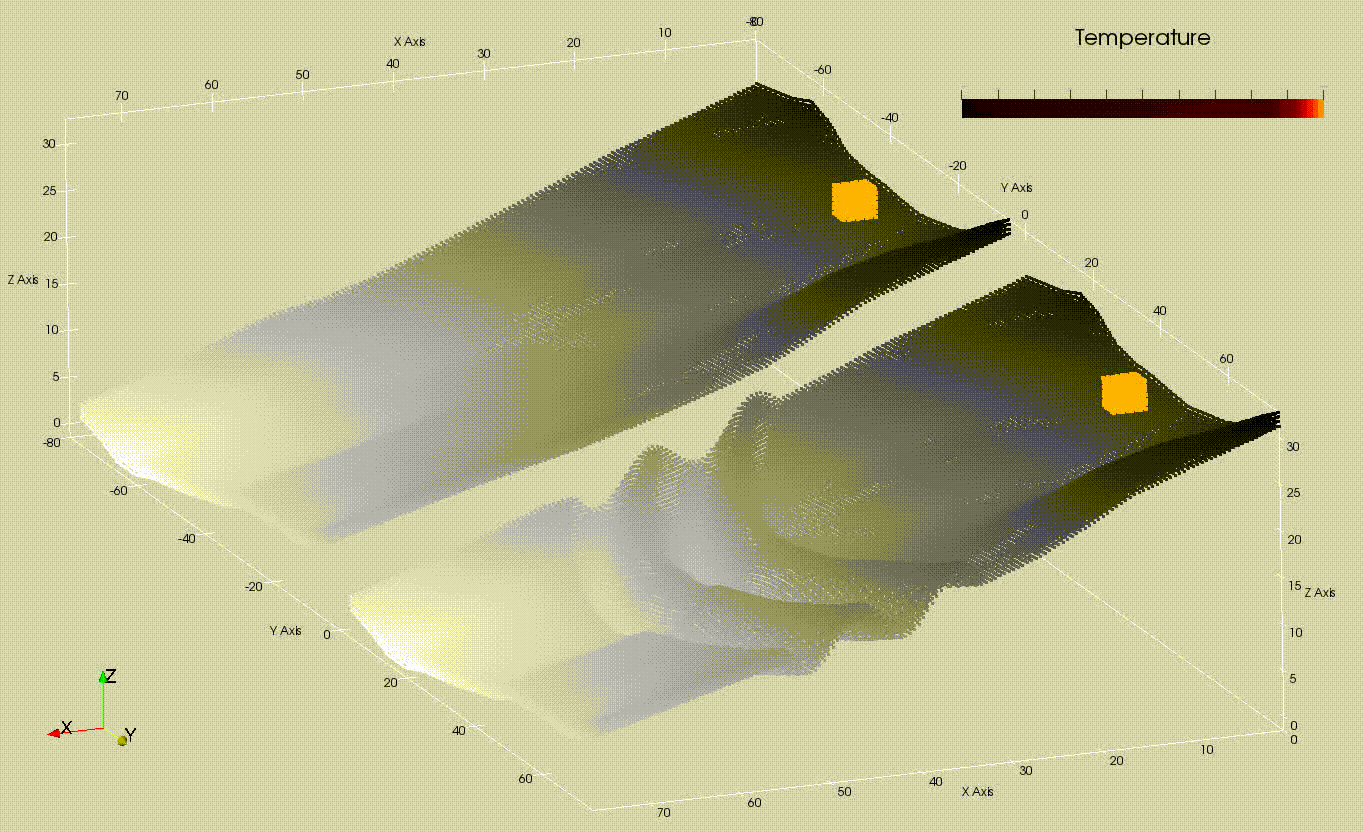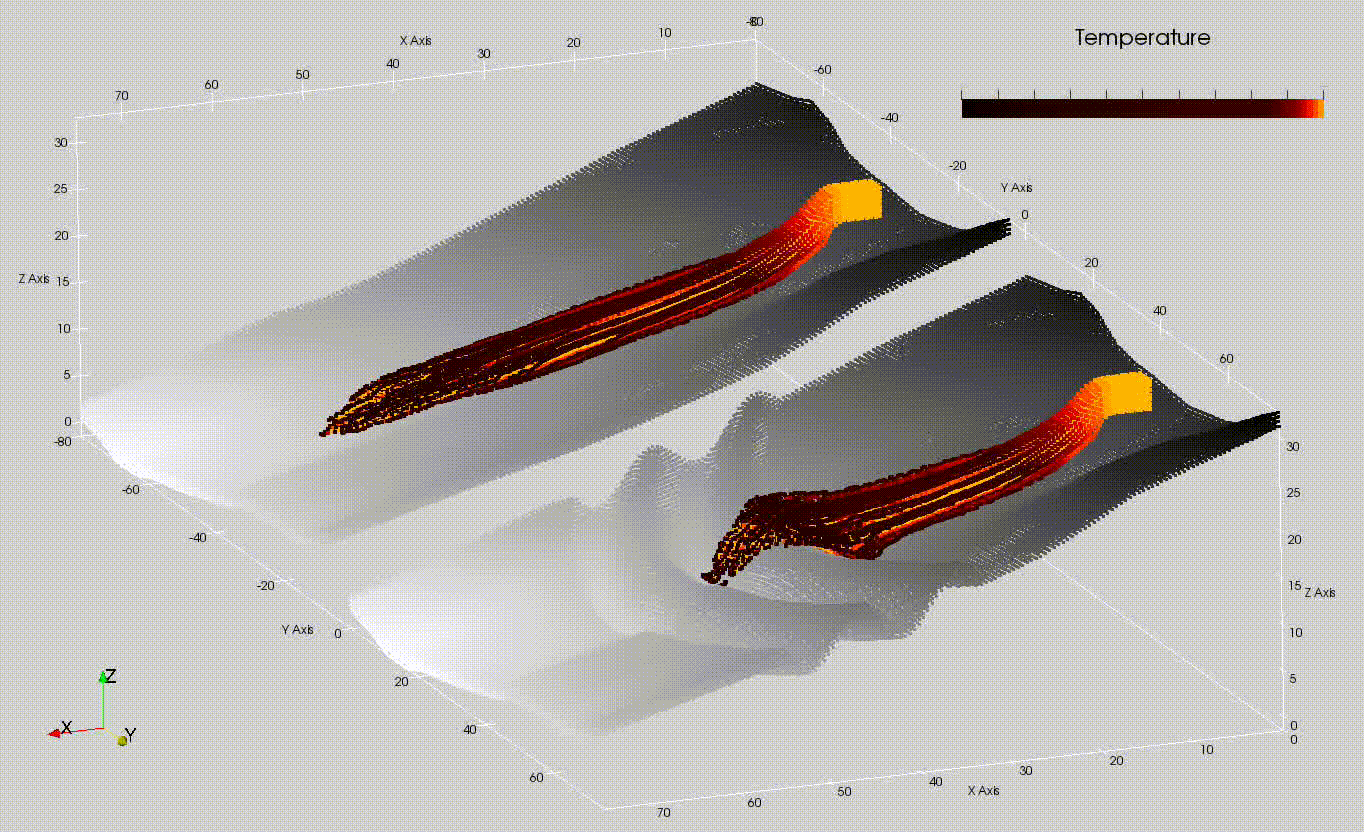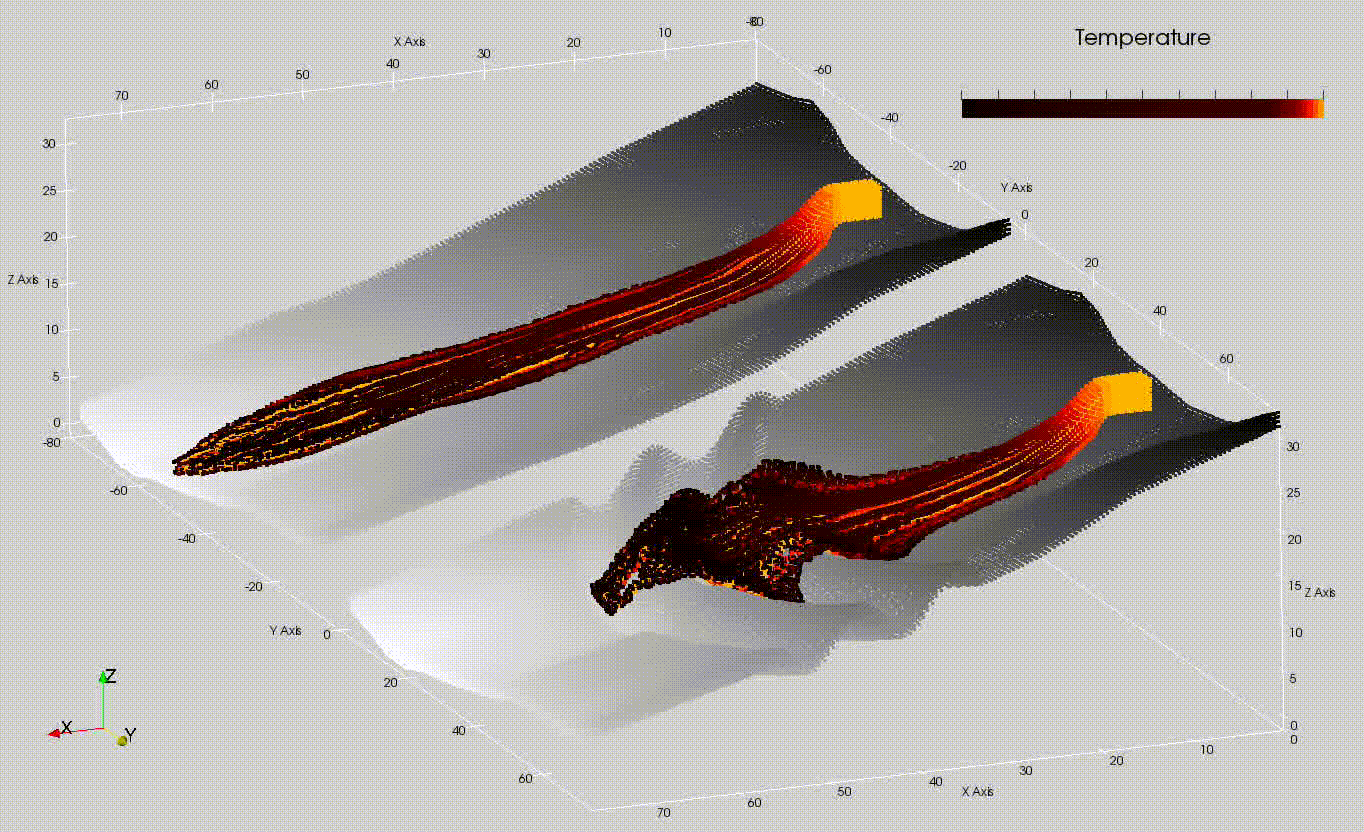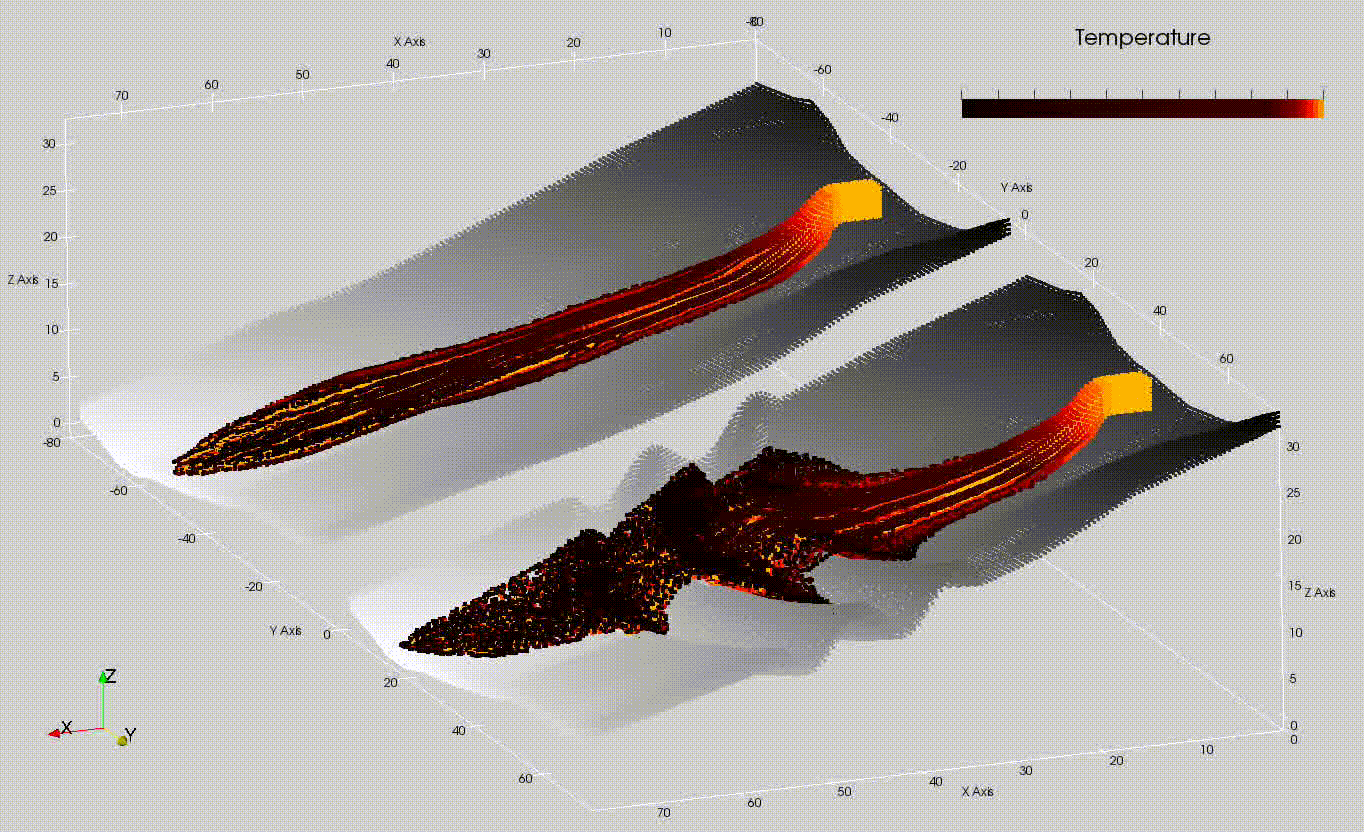 The Models division is engaged in the development of physical-mathematical modeling research of eruptive processes (fig: simulation of lava flows on Etna volcano and potential mitigation plan), aimed at quantitative estimation and monitoring of volcanic hazard. By monitoring, it is meant to both follow the manifestations of the eruption once it has started, and predict the areas potentially threatened by hazardous phenomena by producing different scenarios as eruptive conditions vary. We are active in studying advanced computational physics modeling approaches that also aim to explore the potential of Artificial Intelligence techniques for the development of emulators of physical-mathematical models, aimed at reducing computation times and improving the accuracy of eruptive scenarios. We also have the task of administering and managing the various high-performance computing platforms (parallel and distributed computing, programming on graphics cards) implemented by the UFPV at the Data Processing Center (CED), which are the technological basis for the development of efficient algorithms.
The Models division is engaged in the development of physical-mathematical modeling research of eruptive processes (fig: simulation of lava flows on Etna volcano and potential mitigation plan), aimed at quantitative estimation and monitoring of volcanic hazard. By monitoring, it is meant to both follow the manifestations of the eruption once it has started, and predict the areas potentially threatened by hazardous phenomena by producing different scenarios as eruptive conditions vary. We are active in studying advanced computational physics modeling approaches that also aim to explore the potential of Artificial Intelligence techniques for the development of emulators of physical-mathematical models, aimed at reducing computation times and improving the accuracy of eruptive scenarios. We also have the task of administering and managing the various high-performance computing platforms (parallel and distributed computing, programming on graphics cards) implemented by the UFPV at the Data Processing Center (CED), which are the technological basis for the development of efficient algorithms.
Artificial intelligence
Central to both divisions is the integration of artificial intelligence techniqu es. By leveraging AI algorithms, we seek to extract meaningful information from the vast amounts of satellite observations and to generate more detailed simulations. This procss enabling us to improve predictive capabilities, and ultimately enhance our knowledge on volcanic hazard.
es. By leveraging AI algorithms, we seek to extract meaningful information from the vast amounts of satellite observations and to generate more detailed simulations. This procss enabling us to improve predictive capabilities, and ultimately enhance our knowledge on volcanic hazard.
.png)
